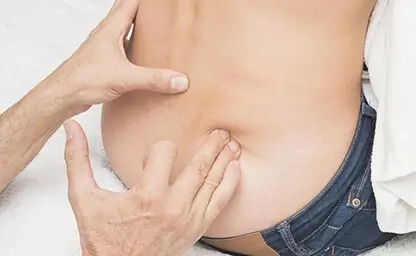
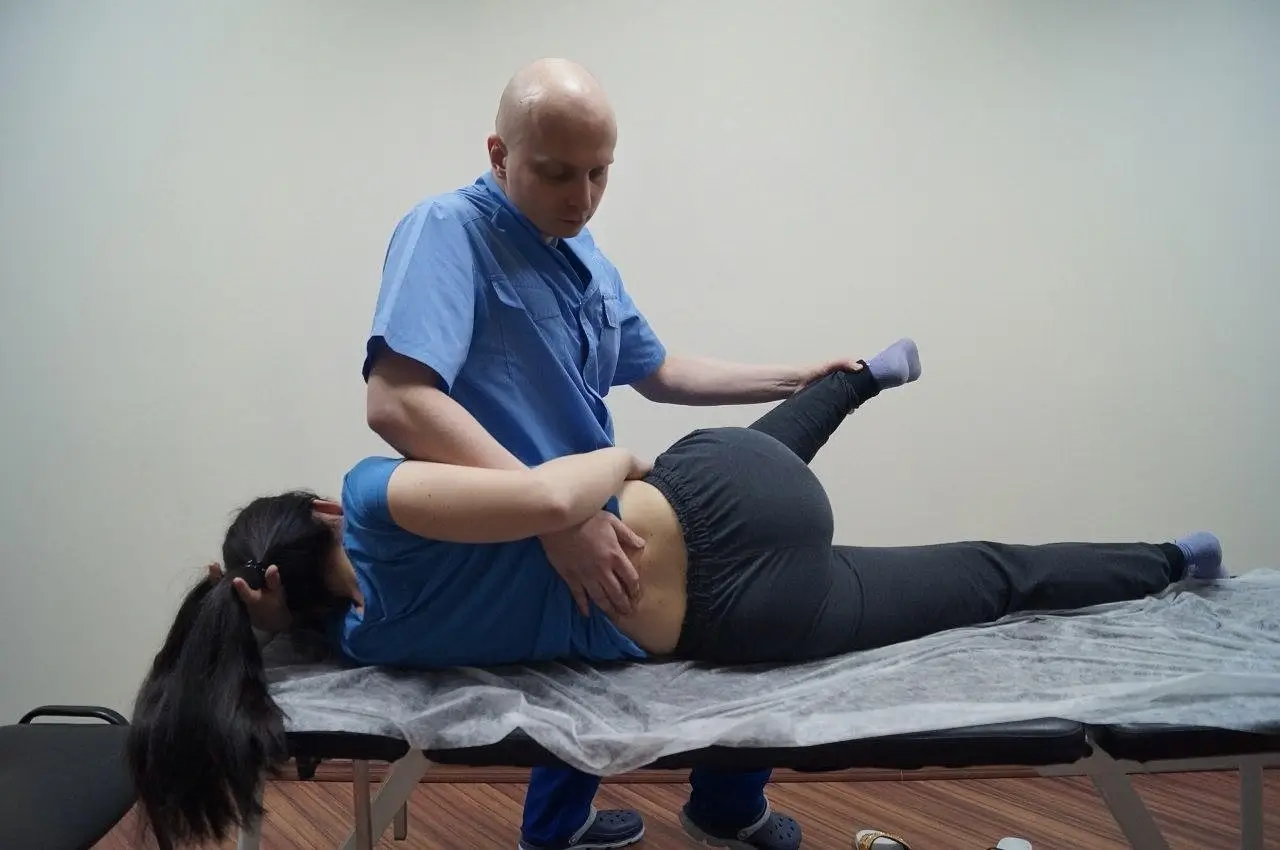
Neurodynamic techniques
NEURODINAMICS
Neurodynamic techniques is by far the most comprehensive and systematized therapy, allowing evaluation of the mechanical mobility of individual nerve trunks, classification of their motion disorders and determination of manual and exercice techniques, as applied to the type and degree of lesion in each individual case. The Australian specialists David Butler and Michael Shacklock made a great contribution to the development of the method.
 Now manual therapists are slowly moving away from unidirectional work to remove functional blocks of spinal-motor segments or restore mobility of peripheral joints. The modern approach is that segmental mobility limitation is only part of the overall picture. As a rule, there is also segmental and multisegmental hypermobility in the pathological process. Restriction of mobility is a consequence of disturbances in the normal dynamics of not only the joints, but also other structures. Such structures include muscles and fascia, ligaments and membranes, nerves and sheaths of the nervous system.
Now manual therapists are slowly moving away from unidirectional work to remove functional blocks of spinal-motor segments or restore mobility of peripheral joints. The modern approach is that segmental mobility limitation is only part of the overall picture. As a rule, there is also segmental and multisegmental hypermobility in the pathological process. Restriction of mobility is a consequence of disturbances in the normal dynamics of not only the joints, but also other structures. Such structures include muscles and fascia, ligaments and membranes, nerves and sheaths of the nervous system.
Thus, methods of diagnostics and treatment that refer to work with the above-mentioned structures are gaining more and more recognition and popularity. At the same time, if the techniques of affecting muscles and muscular-fascial apparatus are widely known and applied for many decades, then clear and systematic manipulations with the nervous tissue appeared only recently (Butler 1991). This explains the fact that clinical neurodynamics, filling a missing gap, has gained universal acceptance and rapid diffusion.
Normal physiological processes and nervous tissue function are possible with optimal mechanical properties of the peripheral nervous system. Similarly, adequate mobility of nerve trunks and their containers ensures natural physiological processes and proper functioning of the nerve tissue. Thus, a deviation in one of the components of this chain affects other links.
Proven effects of neurodynamic therapy
- Passive mobilization of the nervous system reduces pain and intraneural edema
- Works better than static stretching by eliminating adhesions
- Nerve tissue pumping occurs with improvement of blood and lymphatic flow
- Strength and mobility of surrounding muscles also improve
- Often a pronounced immediate analgesic effect is observed
- Stimulates release of endogenous opioids and relief of symptoms
- Normalization of physiological processes through reduction of intraneural edema
- Accelerates nerve recovery and regeneration.
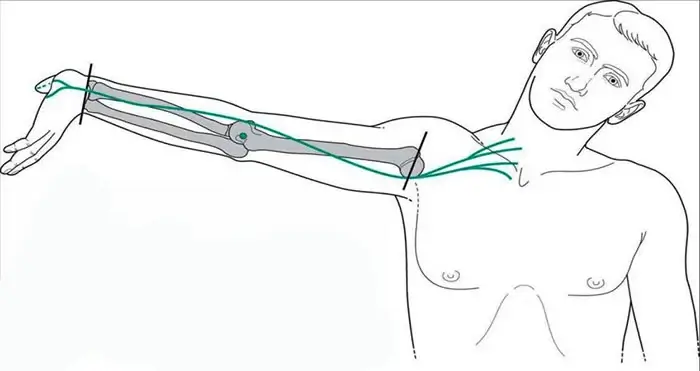
 Thus, clinical neurodynamics provides treatment for patients with the most limited conditions, such as acute radicular syndrome, and for disorders of nerve trunk mobility in athletes of various levels.
Thus, clinical neurodynamics provides treatment for patients with the most limited conditions, such as acute radicular syndrome, and for disorders of nerve trunk mobility in athletes of various levels.
Clinical case:
■ Hands get numb while sleeping.
Neurodynamics as an approach aimed at restoring mobility and functional state of nerve tissues is a qualitative leap in understanding and treating these very frequent disorders. As a practitioner, I can say that the use of these methods of diagnosis (localization of the exact location and direction, the severity of mobility disorders of a particular nerve) and treatment techniques (exact, based on test results, the sequence of necessary actions from comfortable, painless treatment posture, to complex methods of simultaneous treatment of the nerve and surrounding structures) has greatly expanded my understanding and ability to provide safe and effective assistance to patients, including online counseling..
☛ Mulligan's manual therapy.
☛ Neuromuscular treatment - NMT therapy.