Chapman Reflex Points
Neuro-Lymphatic Points
Chapman's neurolymphatic points are special areas on the skin that, when pressed, exert a reflex effect on internal organs and tissues through the nervous and lymphatic systems. These points were discovered by American osteopath Frank Chapman in the 1930s during years of clinical observations.
Chapman found that with certain organ diseases, painful thickenings appear in muscles and fascia in strictly fixed locations. These nodes are sensitive to palpation and disappear after normalization of the corresponding organ function. This is how the connection between neurolymphatic points and internal organs was discovered.
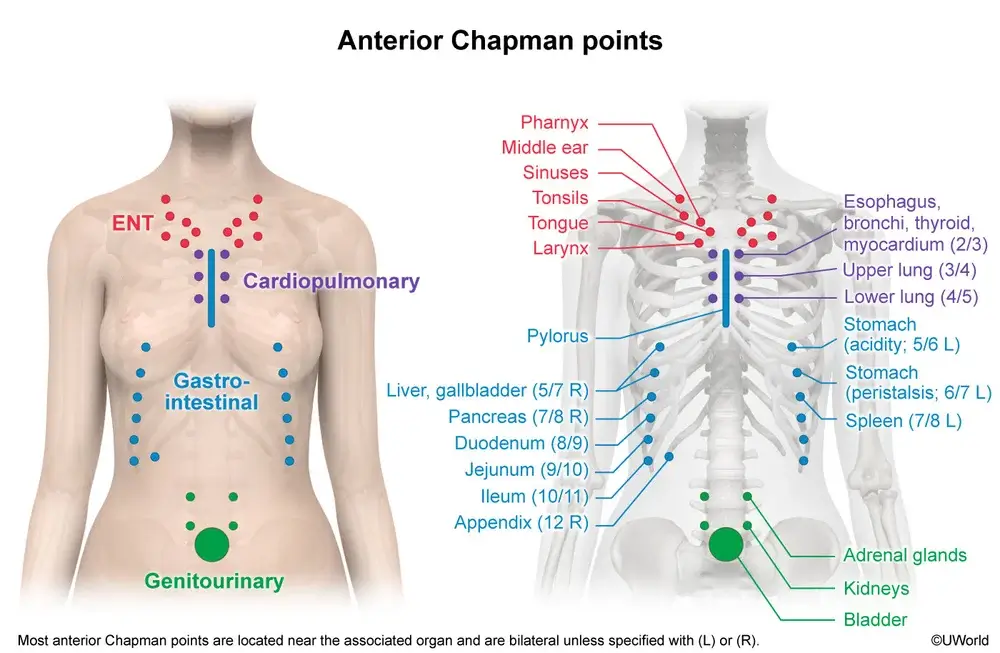 Chapman's neurolymphatic points are localized on the anterior and posterior surfaces of the trunk, extremities, and head. Each point is associated with a specific organ and reflects the state of lymphatic drainage from it. When lymphatic drainage is impaired, the point becomes hypersensitive and painful when pressed. The higher the sensitivity of the point, the more pronounced the pathological process in the corresponding organ.
Chapman's neurolymphatic points are localized on the anterior and posterior surfaces of the trunk, extremities, and head. Each point is associated with a specific organ and reflects the state of lymphatic drainage from it. When lymphatic drainage is impaired, the point becomes hypersensitive and painful when pressed. The higher the sensitivity of the point, the more pronounced the pathological process in the corresponding organ.
Chapman Neurolymphatic Massage
Chapman neurolymphatic massage consists of acting on identified painful points to normalize impaired organ and tissue functions. Treatment is performed by gentle rotational pressure with the fingertip on the point until pain disappears and tissue mobility is restored. Duration of exposure ranges from 20 seconds to 2 minutes.
After treating the anterior points, treatment of corresponding posterior points is performed. Then the anterior points are palpated again - their pain relief indicates therapy effectiveness. In cases of severe disorders, comprehensive treatment may be required - additionally, joint mobilizations and craniosacral therapy are performed. Neurolymphatic therapy can be used as a separate method or in combination with other osteopathic techniques. It not only provides therapeutic effect but also gives information about the condition of internal organs.
History of Method Development
Neurolymphatic reflexes were discovered by American osteopath Frank Chapman in the 1930s. Chapman entered osteopathic school in 1897. After 30 years of practice, he concluded that bone disorders could not explain all pathology in the body. Chapman drew attention to the important role of the lymphatic system and lymphatic drainage disorders in disease development.
As a result of clinical observations, Chapman identified strictly localized points on the skin associated with specific organs. He called them neurolymphatic reflexes, as treatment of these points normalized the functions of corresponding organs. Chapman compiled detailed maps of neurolymphatic point locations on the human body. His son-in-law and follower Charles Owens continued studying the reflexes and systematized the acquired knowledge.
How Therapy is Performed
- Identification of active painful points by palpation of the anterior body surface from head to feet.
- Precise rotational pressure on identified points until tenderness disappears and tissue mobility is restored.
- Reduction of inflammation, decrease of swelling.
- Strengthening of immunity.
- Restoration of impaired metabolic processes.
- Improvement of digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Diagnosis of problematic organs and tissues.
Benefits and Advantages
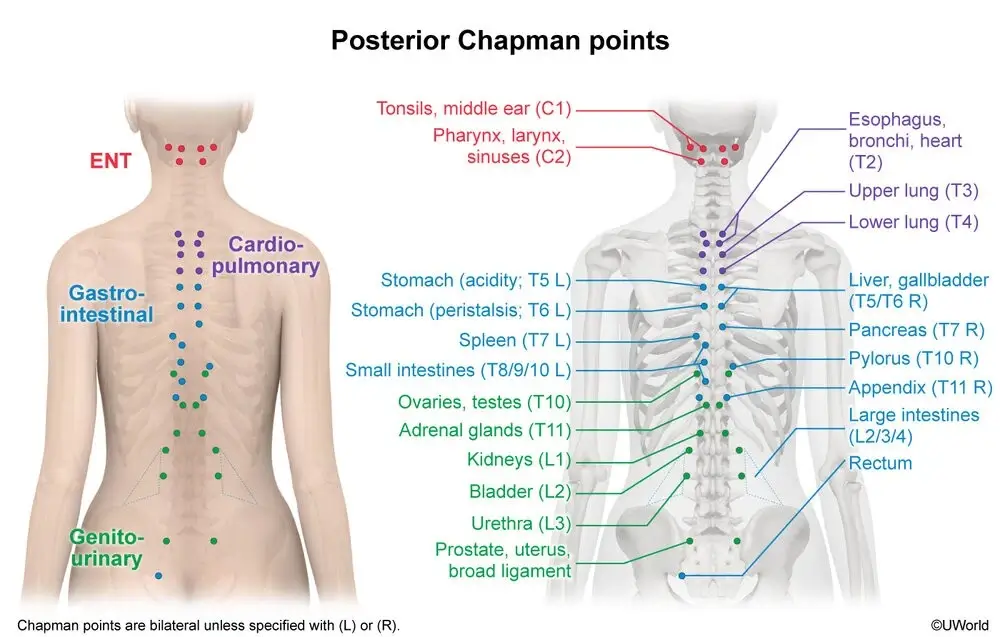 Neurolymphatic therapy is based on the close interconnection of the nervous, lymphatic, and all other body systems. According to Chapman's theory, impaired lymphatic drainage from an organ leads to lymph stagnation and pathology development. This is reflected in the appearance of sensitive thickenings (reflex points) in fascia and muscles connected to the diseased organ.
Neurolymphatic therapy is based on the close interconnection of the nervous, lymphatic, and all other body systems. According to Chapman's theory, impaired lymphatic drainage from an organ leads to lymph stagnation and pathology development. This is reflected in the appearance of sensitive thickenings (reflex points) in fascia and muscles connected to the diseased organ.
The reflex point, therefore, is a projection of the pathological focus on the body surface. By acting on it, one can eliminate lymph stagnation in the organ and normalize its function. This reflex mechanism is due to the presence of somatovisceral connections between skin, muscles, internal organs, and general regulatory body systems.
Place in Osteopathy Manual Medicine OMM
Chapman point therapy is one of the classic osteopathic treatment methods alongside soft tissue, visceral, craniosacral, and other techniques. The peculiarity of this approach is that it allows influence on internal organs through reflex zones on the body surface. This makes it indispensable for osteopathic diagnosis and correction of visceral sphere disorders.
The method is advisable to use at the beginning of a session, after general muscle relaxation. It helps identify problematic organs and prepare tissues for further structural correction. This method can also be used in comprehensive treatment to reinforce the effect of manual and craniosacral therapy, improve lymphatic drainage and metabolic processes.
Advantages of Neurolymphatic Point Therapy
- Pain relief and normalization of internal organ functions.
- Improvement of lymphatic and blood flow, toxin elimination.
- Similar treatment of corresponding posterior points on the back.
- Re-examination of anterior points - their pain relief indicates therapy effectiveness.
- In cases of severe disorders, joint mobilizations and craniosacral therapy are additionally performed.
- Treatment course from 1 to 10-15 sessions depending on the problem.
- Procedure duration 30-60 minutes. Therapy is painless, sensations are pleasant.
Neurolymphatic point therapy is an effective osteopathic method based on reflex connections between skin and internal organs. It allows gentle influence on the visceral sphere and significantly expands manual medicine possibilities. This technique normalizes lymphatic drainage, eliminates inflammation and pain syndromes, optimizes all body systems.
☛ Visceral manipulation techniques.
☛ Theoretical principles of applied kinesiology.